Carbon & LCA
Carbon footprint analysis and Life cycle assessment are two of the most important environmental assessment evaluations.
Carbon Footprint
Carbon Footprint & Neutrality

The process of stopping or reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, especially carbon dioxide, being released into the atmosphere as the result of a process, for example the burning of fossil fuels, is decarbonization.
Carbon Neutrality is when the net emissions of an organisation are equal to zero. If an organisation or an activity etc. is carbon neutral it does not add to the total amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. There are many ways to do this, such as: avoiding, removing, reducing or offsetting emissions. Removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and then storing it is known as carbon sequestration.
A carbon sink is anything that absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases. Forests, Oceans and Soil are the primary natural carbon sinks. Much research is going on in the area of artificial carbon sinks.
Overall global emissions are much higher than the global rate of sequestration hence steps to avoid, reduce and remove the emissions are necessary.
Why is Carbon Management required?
Today the Businesses need visibility on their footprint and the planet needs decarbonization. Carbon Foot printing is now not only an organizational requirement but also a prerequisite for various types of project approvals by the National and International Authorities as a part of sustainable development.
Key approaches to achieve Carbon Neutrality
- Carbon Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Attributes
- Nature-Based Solutions
- Science Based Targets
GHG Inventory

The first step towards Decarbonisation is Carbon Footprint. It is a calculation of a project’s total Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs) over specified period of time, nothing but GHGs emission accounting. GHGs include Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous oxide(N2O, Hydro fluorocarbons (HFCs), Per fluorocarbons (PFCs), Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). GHG accounting should be an integral part of a Business Strategy which has a vision to achieve carbon neutrality. Like financial accounting helps an organisation in financial plan, carbon accounting helps in GHGs management planning. As, what we measure we can manage.
Standards


The calculation and ground work of CO2 footprint are based on standards such as the GHG Protocol and ISO 14064. These are the global standards for quantifying, monitoring, reporting, and verifying GHG emissions.
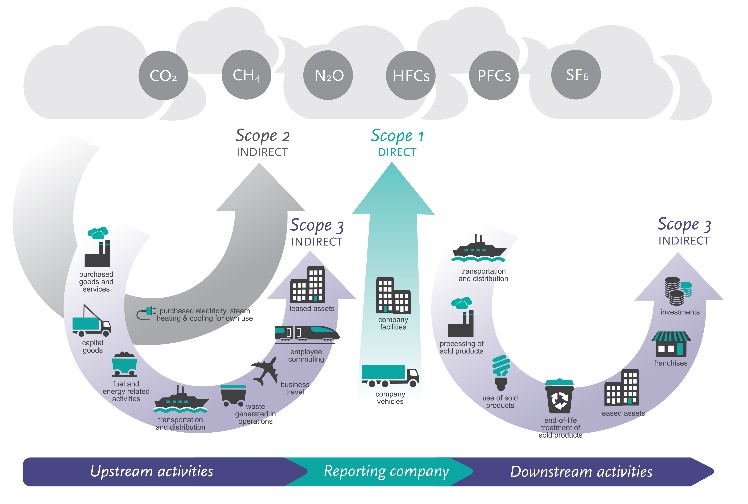
GHG Analysis and Management

- Comprehending the Business, Vision and Mission
- Defining the Organizational Boundary
- Defining the Operational Boundary
- Defining Base Year
- Emission source apportion study
- Identifying and calculating GHG emissions
- Outline Plan for GHG Emission Reduction
- Target setting
- Reporting GHG Emissions
- Verification of GHG Emissions
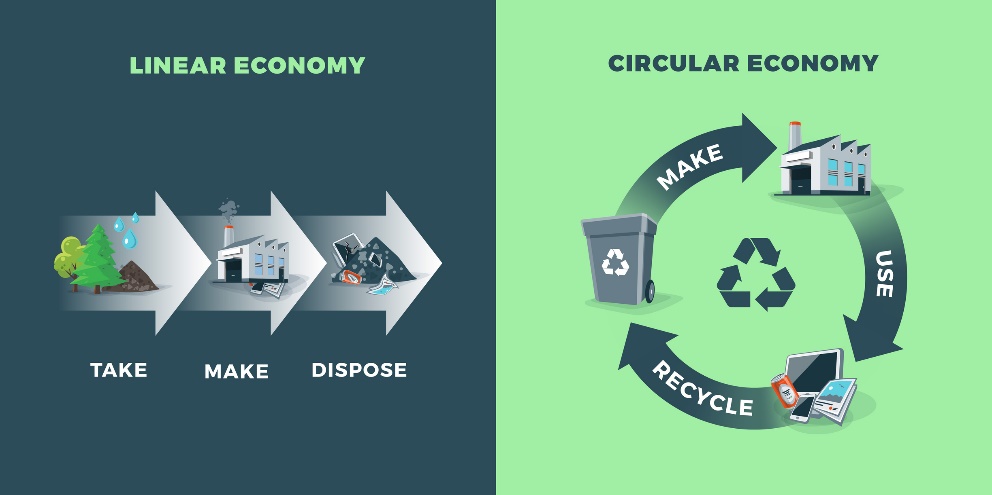
Life Cycle Analysis
What is LCA?
A Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) maps the environmental impact of a product or an organization. This environmental impact is measured in different categories such as climate warming potential, ozone depletion, eco- or human toxicological effects, or land-use change. It is a technique for assessing the environmental aspects and potential impacts associated with a product or a process. The scope of different LCA studies can vary. Hence, Cradle to Gate, Cradle to Grave, Cradle to Cradle etc. scopes will be applicable based on the intent of the LCA.
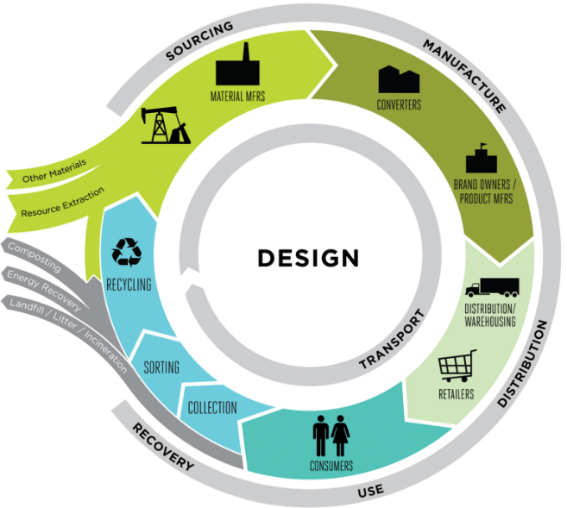
Why is LCA required?

The information provided by a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) provides the opportunity to make environmentally conscious choices in the design of a product or in further business decisions, with the aim of minimizing the environmental impact. It contributes to a company’s sustainability strategy and can be used in internal and external communication. LCAs are not general and often need to be customized as each entity has its own unique process and administration. Hence tailor-made solutions are necessary. The authenticity of an analysis is primarily based on the LCA database, its pertinence to the project and the Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA) methods adopted.
The applications of LCA are:
- Comprehensible comparative between alternatives
- Environmental product declaration (EPD) as per ISO 14025
- Environmental Impact assessment in various categories
- Carbon reporting
- Useful in ESG reporting
- Useful in certain GBC Certifications
- Verification of impact reduction claims of proclaimed green/eco-friendly options v/s other options
- Strategic decision-making based on the environmental data
- Declaration of environmental impact
- Evidence of organisations sustainability actions and their impacts
- Obliging the requisites of tenders or certification projects
Our Services
We have expertise in LCA analysis. We can help you to ascertain the environmental impact of a single product or an entire organization. In collaboration with the client, we take every aspect of the business into account and ensure that the life cycle assessment is complete, accurate, authentic and in accordance with all the (international) standards.
Environmental, Social & Governance Factors
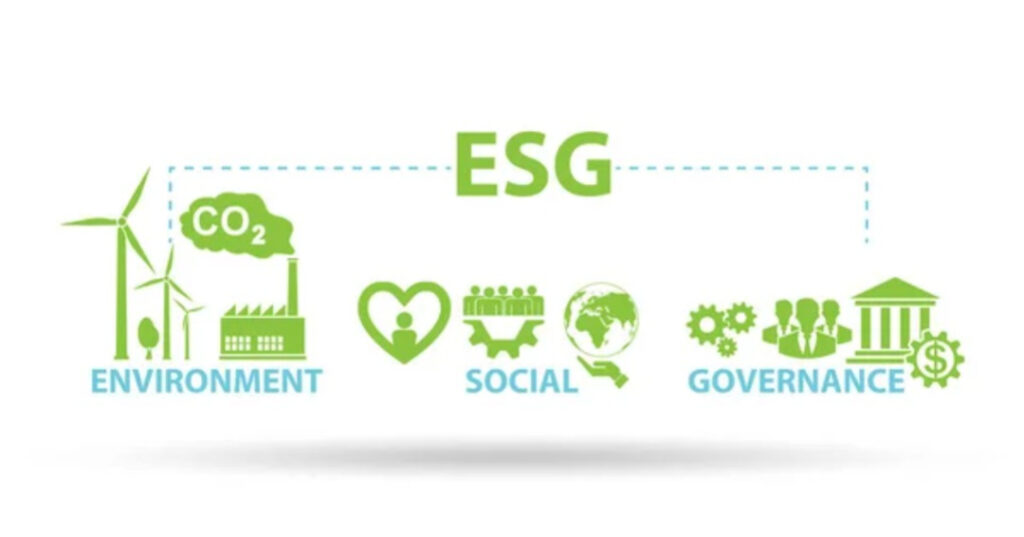
What is ESG?

Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are a set of standards for a company’s operations. Environmental criteria consider how a company performs in the environmental aspects such as pollution control, impact reduction, mitigation measures and protection of environment. Social criteria examine how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. Governance deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
When you put ESG at the very heart of your operation, you take bold steps towards a model that will deliver sustainable business advantage and measurable value.
In the current business scenario, it is becoming crucial for companies to report and improve their ESG data as per the interest and demands of the stakeholders, markets and regulatory authorities. Data management is the key to access, declare and accurately manage a company’s sustainability performance.
The knowledge of ESG reporting, which standards to follow and techniques is often required by such companies to streamline and avoid complications in the process.
Why is ESG Required?
Sustainability reporting declares the company’s performance in governance, environmental, and social areas, which help the actors to know the impact on stakeholders and help assess improvement opportunities.
There are established business benefits to sustainability reporting and taking climate action. The active disclosure and communication of a company’s environmental, social and governmental (ESG) impacts is significant to future-proofing your business success in the circular economy. It enables you to take proactive measures and take advanced best practices to improve value.
Main benefits of ESG reporting
Additionally, reporting, managing and improving the ESG data allows stakeholders and investors to gain insight into your business and maximize your positive impact.
- Improving stakeholder and investor confidence
- To attract investors
- Surpassing the Regulatory requirements
- Risk management in the ESG purview
- Reputation building
- Boosting employee morale
- Acquiring a competitive edge
Our Services
We help the companies regardless of their size, industry or sustainability experience in effective ESG reporting. We help the client to construct an ESG report, and be more productive and better organized in their ESG management. This means our clients collaborate, share and manage their ESG data in a transparent, accurate manner and with security which in turn allows for greater value.
Carbon Footprint
Why is Carbon Management required?
Today the Businesses need visibility on their footprint and the planet needs decarbonization. Carbon Foot printing is now not only an organizational requirement but also a prerequisite for various types of project approvals by the National and International Authorities as a part of sustainable development.
Carbon Footprint & Neutrality
The process of stopping or reducing carbon gases, especially carbon dioxide, being released into the atmosphere as the result of a process, for example the burning of fossil fuels, is decarbonization.
Carbon Neutrality is when the net emissions of an organisation are equal to zero. If an organisation or an activity etc. is carbon neutral it does not add to the total amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. There are many ways to do this, such as: avoiding, removing, reducing or offsetting emissions. Removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and then storing it is known as carbon sequestration.
A carbon sink is anything that absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases. Forests, Oceans and Soil are the primary natural carbon sinks. Much research is going on in the area of artificial carbon sinks.
Overall global emissions are much higher than the global rate of sequestration hence steps to avoid, reduce and remove the emissions are necessary.
GHG Inventory
The first step towards Decarbonisation is Carbon Footprint. It is a calculation of a project’s total Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs) over specified period of time, nothing but GHGs emission accounting. GHGs include Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous oxide(N2O, Hydro fluorocarbons (HFCs), Per fluorocarbons (PFCs), Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). GHG accounting should be an integral part of a Business Strategy which has a vision to achieve carbon neutrality. Like financial accounting helps an organisation in financial plan, carbon accounting helps in GHGs management planning. As, what we measure we can manage.
